TODAY’S PATENT – METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER USING ANTI-PD-1 ANTIBODIES
The invention relates to isolated monoclonal antibodies, specifically human monoclonal antibodies that have a high affinity for PD-1. Additionally, the invention provides nucleic acid molecules that encode these antibodies, expression vectors, host cells, and methods for expressing the antibodies. Immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules, and pharmaceutical compositions that include these antibodies are also provided.
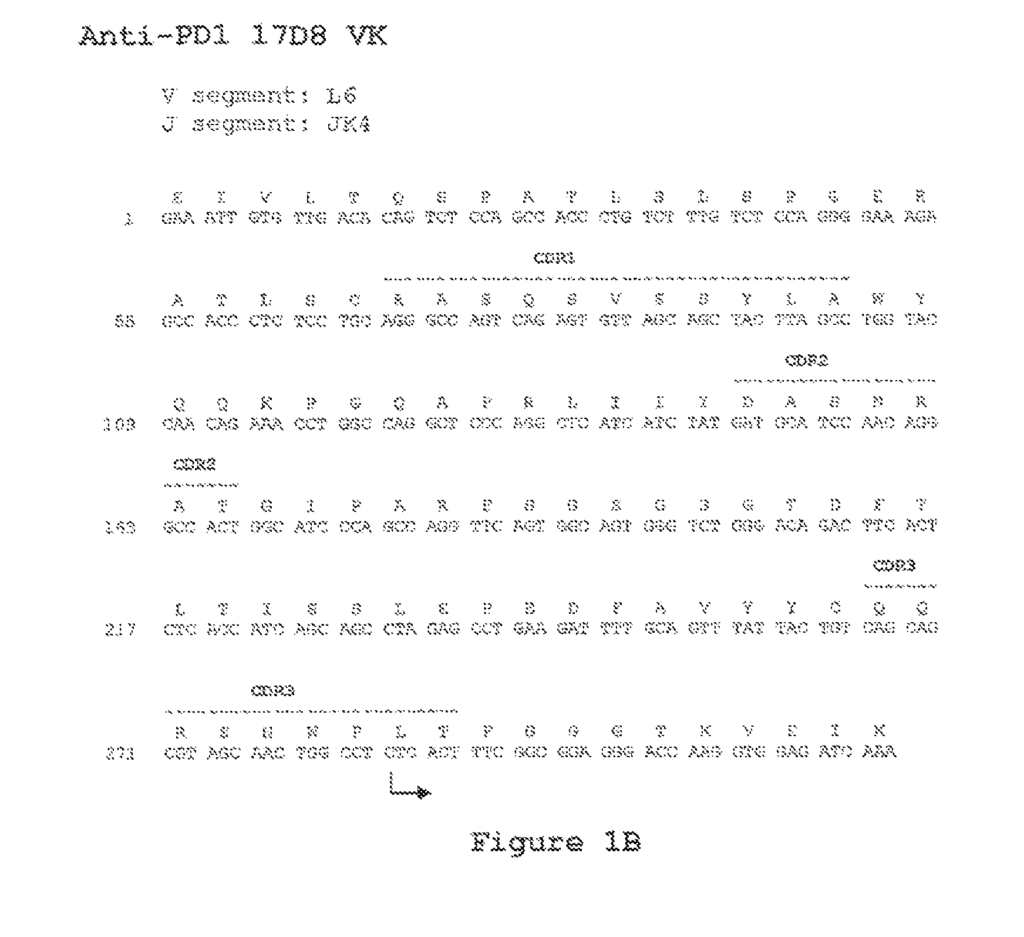
The invention includes methods for detecting PD-1 and for treating various diseases, such as cancer and infectious diseases, using anti-PD-1 antibodies. Furthermore, the invention provides methods for using a combination immunotherapy, such as anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies, to treat hyperproliferative diseases, including cancer. Additionally, the invention provides methods for altering adverse events related to treatment with these antibodies.
It was invented by Alan J. Korman and others and was patented by USPTO on 21st July 2015 with the serial number US9084776B2. The antibodies of the invention exhibit high affinity binding to human PD-1 and do not cross-react with human CD28, CTLA-4, or ICOS, making them desirable. The antibodies have also been shown to modulate immune responses. The invention provides a method of inhibiting tumor cell growth in vivo using anti-PD-1 antibodies.

 +1 888 890 6411
+1 888 890 6411